
IRR is commonly used in capital budgeting to discern the rate of return on the estimated cash flows arising from an expected investment.
DISCOUNTED CASHFLOWS SERIES
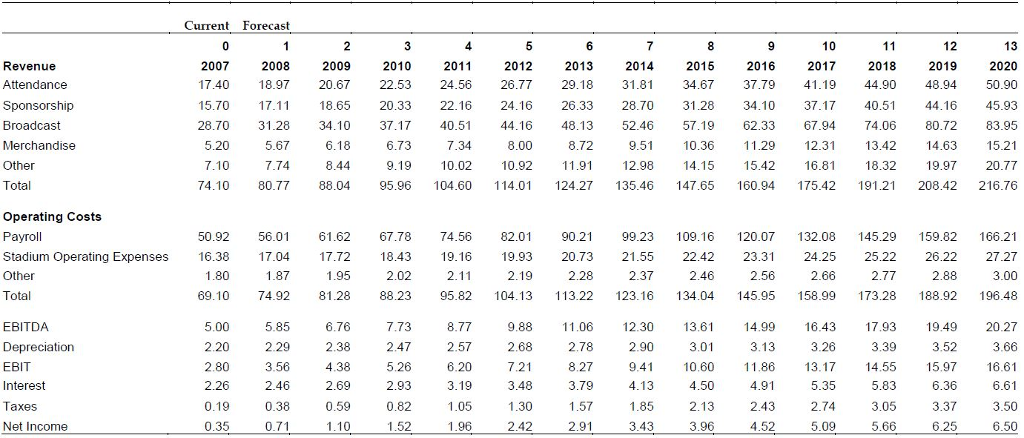
The internal rate of return (IRR) is the rate of return at which the present value of a series of future cash flows equals the present value of all associated costs. R = The rate of return What is the Internal Rate of Return? To calculate net present value, we use the following formula: NPV is commonly used in the analysis of capital purchasing requests, to see if an initial payment for fixed assets and other expenditures will generate net positive cash flows. It can also be used to compare several such cash flows to decide which has the largest present value. Net present value (NPV) analysis is useful for determining the current value of a stream of cash flows that extend out into the future. Two analysis methods that employ the discounted cash flow concept are net present value and the internal rate of return, which are described next.
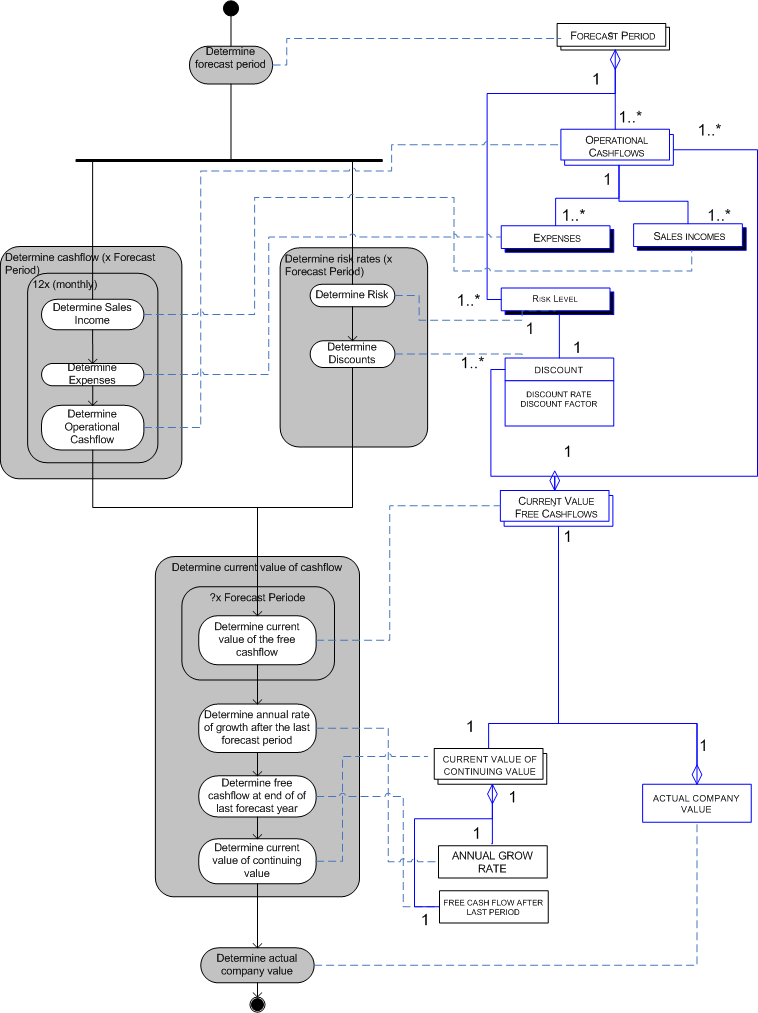
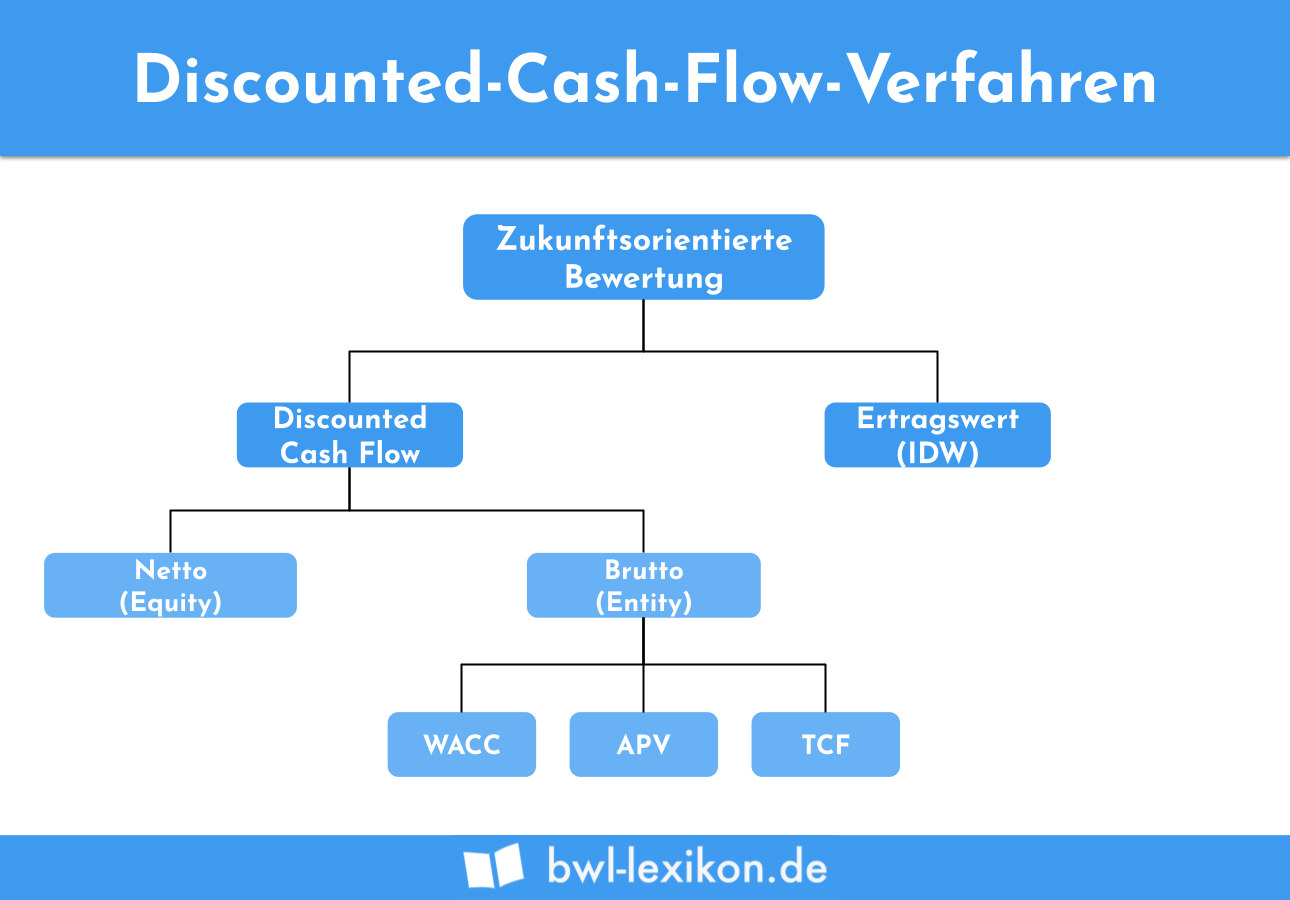
The interest income in this example represents the time value of money. If she were instead to not have access to that cash for one year, then she would lose the $1,000 of interest income. If a person owns $10,000 now and invests it at an interest rate of 10%, then she will have earned $1,000 by having use of the money for one year. The only way for someone to agree to a delayed payment is to pay them for the privilege, which is known as interest income. The reason is that someone who agrees to receive payment at a later date foregoes the ability to invest that cash right now. The foundation of discounted cash flow analysis is the concept that cash received today is more valuable than cash received at some point in the future. This concept is useful for calculating the value of a prospective acquisition, of a possible annuity investment, or of a fixed asset purchase. Multiplying this discount by each future cash flow results in an amount that is, in aggregate, the present value of all future cash flows.īy calculating the discounted cash flows for a number of different investment choices, one can select the alternative that results in the greatest discounted cash flows. Under the DCF method, one applies a discount rate to each periodic cash flow that is derived from an entity's cost of capital. This approach can be used to derive the value of an investment.

Many are regional banks that serve the needs of the agriculture and tourism sectors. Third Tier: Called the seasonal credit program, this one serves smaller financial institutions which experience higher seasonal variations in their cash flows.Institutions in this tier are smaller and may not be as financially healthy as the ones that use the primary tier. It is usually set 50 basis points higher than the primary rate (one percentage point = 100 basis points). Second Tier: Called the secondary credit program, it offers similar loans to institutions that do not qualify for the primary rate.This primary credit discount rate is usually set above existing market interest rates which may be available from other banks or other sources of similar short-term debt. First Tier: Called the primary credit program, this tier provides capital to financially sound banks with good credit records.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
